Gait Recognition
Gait recognition is the process of identifying and verifying individuals based on their walking patterns.
Papers and Code
Affinity Contrastive Learning for Skeleton-based Human Activity Understanding
Jan 23, 2026In skeleton-based human activity understanding, existing methods often adopt the contrastive learning paradigm to construct a discriminative feature space. However, many of these approaches fail to exploit the structural inter-class similarities and overlook the impact of anomalous positive samples. In this study, we introduce ACLNet, an Affinity Contrastive Learning Network that explores the intricate clustering relationships among human activity classes to improve feature discrimination. Specifically, we propose an affinity metric to refine similarity measurements, thereby forming activity superclasses that provide more informative contrastive signals. A dynamic temperature schedule is also introduced to adaptively adjust the penalty strength for various superclasses. In addition, we employ a margin-based contrastive strategy to improve the separation of hard positive and negative samples within classes. Extensive experiments on NTU RGB+D 60, NTU RGB+D 120, Kinetics-Skeleton, PKU-MMD, FineGYM, and CASIA-B demonstrate the superiority of our method in skeleton-based action recognition, gait recognition, and person re-identification. The source code is available at https://github.com/firework8/ACLNet.
* Accepted by TBIOM
Language-Guided and Motion-Aware Gait Representation for Generalizable Recognition
Jan 17, 2026Gait recognition is emerging as a promising technology and an innovative field within computer vision. However, existing methods typically rely on complex architectures to directly extract features from images and apply pooling operations to obtain sequence-level representations. Such designs often lead to overfitting on static noise (e.g., clothing), while failing to effectively capture dynamic motion regions.To address the above challenges, we present a Language guided and Motion-aware gait recognition framework, named LMGait.In particular, we utilize designed gait-related language cues to capture key motion features in gait sequences.
Synthetic Data Guided Feature Selection for Robust Activity Recognition in Older Adults
Jan 21, 2026Physical activity during hip fracture rehabilitation is essential for mitigating long-term functional decline in geriatric patients. However, it is rarely quantified in clinical practice. Existing continuous monitoring systems with commercially available wearable activity trackers are typically developed in middle-aged adults and therefore perform unreliably in older adults with slower and more variable gait patterns. This study aimed to develop a robust human activity recognition (HAR) system to improve continuous physical activity recognition in the context of hip fracture rehabilitation. 24 healthy older adults aged over 80 years were included to perform activities of daily living (walking, standing, sitting, lying down, and postural transfers) under simulated free-living conditions for 75 minutes while wearing two accelerometers positioned on the lower back and anterior upper thigh. Model robustness was evaluated using leave-one-subject-out cross-validation. The synthetic data demonstrated potential to improve generalization across participants. The resulting feature intervention model (FIM), aided by synthetic data guidance, achieved reliable activity recognition with mean F1-scores of 0.896 for walking, 0.927 for standing, 0.997 for sitting, 0.937 for lying down, and 0.816 for postural transfers. Compared with a control condition model without synthetic data, the FIM significantly improved the postural transfer detection, i.e., an activity class of high clinical relevance that is often overlooked in existing HAR literature. In conclusion, these preliminary results demonstrate the feasibility of robust activity recognition in older adults. Further validation in hip fracture patient populations is required to assess the clinical utility of the proposed monitoring system.
Learning Geometric Invariance for Gait Recognition
Jan 09, 2026The goal of gait recognition is to extract identity-invariant features of an individual under various gait conditions, e.g., cross-view and cross-clothing. Most gait models strive to implicitly learn the common traits across different gait conditions in a data-driven manner to pull different gait conditions closer for recognition. However, relatively few studies have explicitly explored the inherent relations between different gait conditions. For this purpose, we attempt to establish connections among different gait conditions and propose a new perspective to achieve gait recognition: variations in different gait conditions can be approximately viewed as a combination of geometric transformations. In this case, all we need is to determine the types of geometric transformations and achieve geometric invariance, then identity invariance naturally follows. As an initial attempt, we explore three common geometric transformations (i.e., Reflect, Rotate, and Scale) and design a $\mathcal{R}$eflect-$\mathcal{R}$otate-$\mathcal{S}$cale invariance learning framework, named ${\mathcal{RRS}}$-Gait. Specifically, it first flexibly adjusts the convolution kernel based on the specific geometric transformations to achieve approximate feature equivariance. Then these three equivariant-aware features are respectively fed into a global pooling operation for final invariance-aware learning. Extensive experiments on four popular gait datasets (Gait3D, GREW, CCPG, SUSTech1K) show superior performance across various gait conditions.
Beyond Motion Pattern: An Empirical Study of Physical Forces for Human Motion Understanding
Dec 23, 2025



Human motion understanding has advanced rapidly through vision-based progress in recognition, tracking, and captioning. However, most existing methods overlook physical cues such as joint actuation forces that are fundamental in biomechanics. This gap motivates our study: if and when do physically inferred forces enhance motion understanding? By incorporating forces into established motion understanding pipelines, we systematically evaluate their impact across baseline models on 3 major tasks: gait recognition, action recognition, and fine-grained video captioning. Across 8 benchmarks, incorporating forces yields consistent performance gains; for example, on CASIA-B, Rank-1 gait recognition accuracy improved from 89.52% to 90.39% (+0.87), with larger gain observed under challenging conditions: +2.7% when wearing a coat and +3.0% at the side view. On Gait3D, performance also increases from 46.0% to 47.3% (+1.3). In action recognition, CTR-GCN achieved +2.00% on Penn Action, while high-exertion classes like punching/slapping improved by +6.96%. Even in video captioning, Qwen2.5-VL's ROUGE-L score rose from 0.310 to 0.339 (+0.029), indicating that physics-inferred forces enhance temporal grounding and semantic richness. These results demonstrate that force cues can substantially complement visual and kinematic features under dynamic, occluded, or appearance-varying conditions.
Is Visual Realism Enough? Evaluating Gait Biometric Fidelity in Generative AI Human Animation
Dec 22, 2025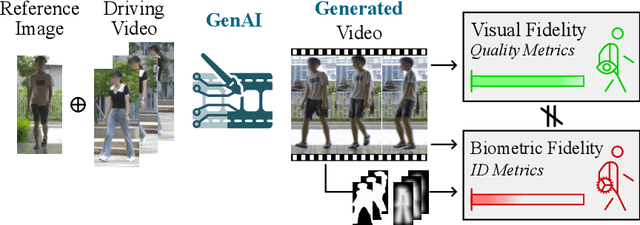
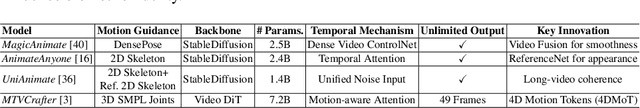
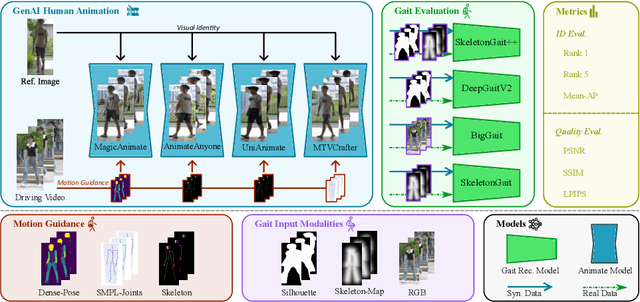
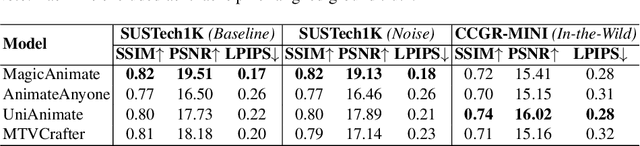
Generative AI (GenAI) models have revolutionized animation, enabling the synthesis of humans and motion patterns with remarkable visual fidelity. However, generating truly realistic human animation remains a formidable challenge, where even minor inconsistencies can make a subject appear unnatural. This limitation is particularly critical when AI-generated videos are evaluated for behavioral biometrics, where subtle motion cues that define identity are easily lost or distorted. The present study investigates whether state-of-the-art GenAI human animation models can preserve the subtle spatio-temporal details needed for person identification through gait biometrics. Specifically, we evaluate four different GenAI models across two primary evaluation tasks to assess their ability to i) restore gait patterns from reference videos under varying conditions of complexity, and ii) transfer these gait patterns to different visual identities. Our results show that while visual quality is mostly high, biometric fidelity remains low in tasks focusing on identification, suggesting that current GenAI models struggle to disentangle identity from motion. Furthermore, through an identity transfer task, we expose a fundamental flaw in appearance-based gait recognition: when texture is disentangled from motion, identification collapses, proving current GenAI models rely on visual attributes rather than temporal dynamics.
RobustGait: Robustness Analysis for Appearance Based Gait Recognition
Nov 17, 2025



Appearance-based gait recognition have achieved strong performance on controlled datasets, yet systematic evaluation of its robustness to real-world corruptions and silhouette variability remains lacking. We present RobustGait, a framework for fine-grained robustness evaluation of appearance-based gait recognition systems. RobustGait evaluation spans four dimensions: the type of perturbation (digital, environmental, temporal, occlusion), the silhouette extraction method (segmentation and parsing networks), the architectural capacities of gait recognition models, and various deployment scenarios. The benchmark introduces 15 corruption types at 5 severity levels across CASIA-B, CCPG, and SUSTech1K, with in-the-wild validation on MEVID, and evaluates six state-of-the-art gait systems. We came across several exciting insights. First, applying noise at the RGB level better reflects real-world degradation, and reveal how distortions propagate through silhouette extraction to the downstream gait recognition systems. Second, gait accuracy is highly sensitive to silhouette extractor biases, revealing an overlooked source of benchmark bias. Third, robustness is dependent on both the type of perturbation and the architectural design. Finally, we explore robustness-enhancing strategies, showing that noise-aware training and knowledge distillation improve performance and move toward deployment-ready systems.
Gait Recognition via Collaborating Discriminative and Generative Diffusion Models
Nov 09, 2025Gait recognition offers a non-intrusive biometric solution by identifying individuals through their walking patterns. Although discriminative models have achieved notable success in this domain, the full potential of generative models remains largely underexplored. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{CoD$^2$}, a novel framework that combines the data distribution modeling capabilities of diffusion models with the semantic representation learning strengths of discriminative models to extract robust gait features. We propose a Multi-level Conditional Control strategy that incorporates both high-level identity-aware semantic conditions and low-level visual details. Specifically, the high-level condition, extracted by the discriminative extractor, guides the generation of identity-consistent gait sequences, whereas low-level visual details, such as appearance and motion, are preserved to enhance consistency. Furthermore, the generated sequences facilitate the discriminative extractor's learning, enabling it to capture more comprehensive high-level semantic features. Extensive experiments on four datasets (SUSTech1K, CCPG, GREW, and Gait3D) demonstrate that CoD$^2$ achieves state-of-the-art performance and can be seamlessly integrated with existing discriminative methods, yielding consistent improvements.
Dynamic Black-box Backdoor Attacks on IoT Sensory Data
Nov 18, 2025Sensor data-based recognition systems are widely used in various applications, such as gait-based authentication and human activity recognition (HAR). Modern wearable and smart devices feature various built-in Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) sensors, and such sensor-based measurements can be fed to a machine learning-based model to train and classify human activities. While deep learning-based models have proven successful in classifying human activity and gestures, they pose various security risks. In our paper, we discuss a novel dynamic trigger-generation technique for performing black-box adversarial attacks on sensor data-based IoT systems. Our empirical analysis shows that the attack is successful on various datasets and classifier models with minimal perturbation on the input data. We also provide a detailed comparative analysis of performance and stealthiness to various other poisoning techniques found in backdoor attacks. We also discuss some adversarial defense mechanisms and their impact on the effectiveness of our trigger-generation technique.
Understanding the Representation of Older Adults in Motion Capture Locomotion Datasets
Nov 12, 2025The Internet of Things (IoT) sensors have been widely employed to capture human locomotions to enable applications such as activity recognition, human pose estimation, and fall detection. Motion capture (MoCap) systems are frequently used to generate ground truth annotations for human poses when training models with data from wearable or ambient sensors, and have been shown to be effective to synthesize data in these modalities. However, the representation of older adults, an increasingly important demographic in healthcare, in existing MoCap locomotion datasets has not been thoroughly examined. This work surveyed 41 publicly available datasets, identifying eight that include older adult motions and four that contain motions performed by younger actors annotated as old style. Older adults represent a small portion of participants overall, and few datasets provide full-body motion data for this group. To assess the fidelity of old-style walking motions, quantitative metrics are introduced, defining high fidelity as the ability to capture age-related differences relative to normative walking. Using gait parameters that are age-sensitive, robust to noise, and resilient to data scarcity, we found that old-style walking motions often exhibit overly controlled patterns and fail to faithfully characterize aging. These findings highlight the need for improved representation of older adults in motion datasets and establish a method to quantitatively evaluate the quality of old-style walking motions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge